authors
Youngwook Paul Kwon, Hyojin Kim, Goran Konjevod, and Sara McMains
abstract
We present a novel descriptor algorithm (DUDE) using line/point duality and a randomization strategy that provides simple but robust, consistent feature extraction and correspondence. Using duality enables us to effectively capture a distribution of line segments, and the proposed randomization strategy improves repeatability over existing techniques by generating more line features in common between two images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach using a challenging set of disparate image pairs, and show that the DUDE descriptor performs comparably to state-of-the-art methods with significantly less computation expense.
paper
data
result
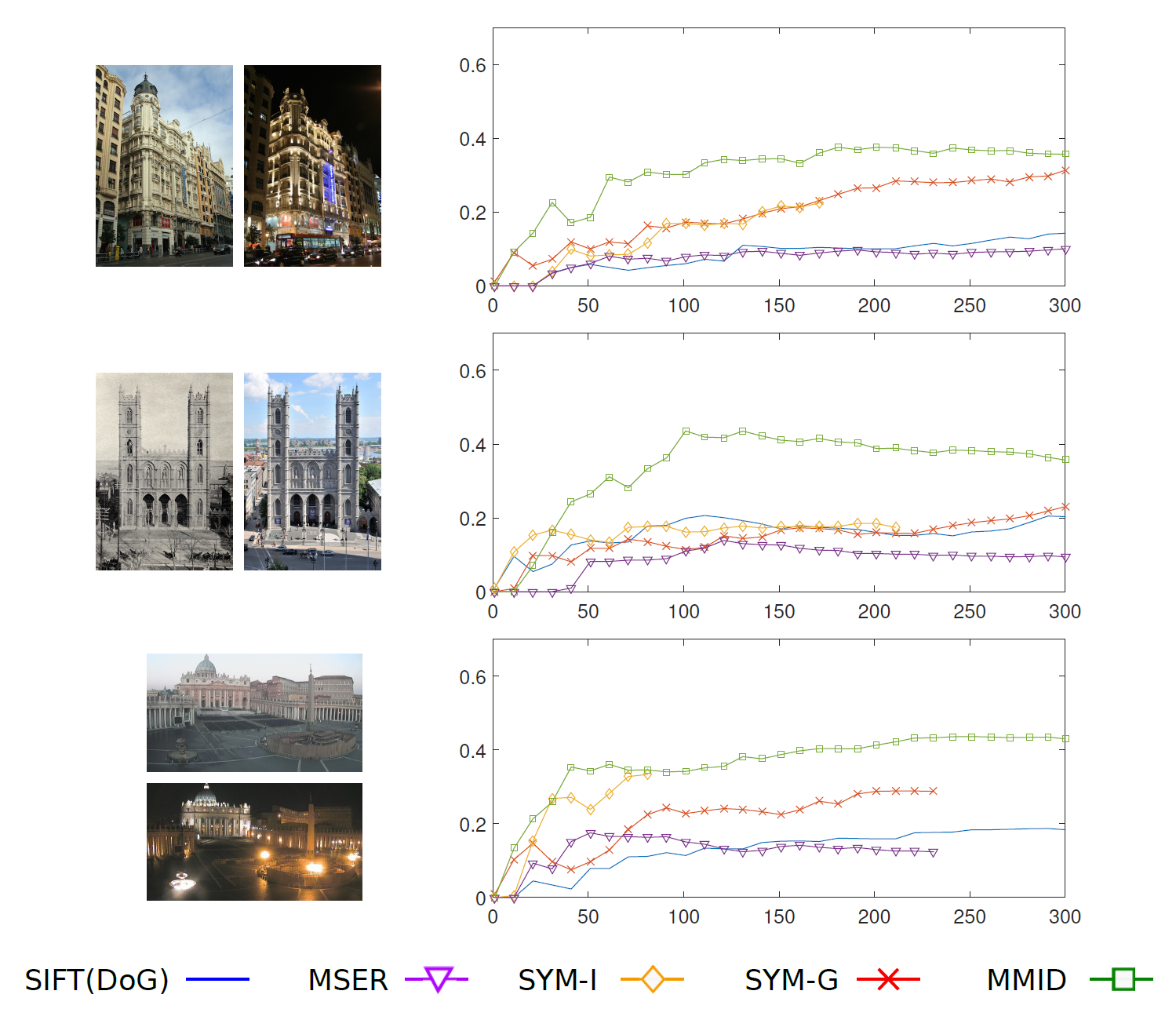
- Feature detection repeatability In the figure below, we illustrate precision-recall curves for a few image pairs. The choice example image pairs are the same as in [3]. Each row represents a feature detection type. DUDE (black) and DUDE-F (green) show overall good performance except for the last image pair, where most of algorithms do not work well. However, when detection is perfect (GRID), DUDE and DUDE-F outperform their competitors. Because DUDE-F has one more step than DUDE, it is natural for DUDE-F to be better than DUDE.
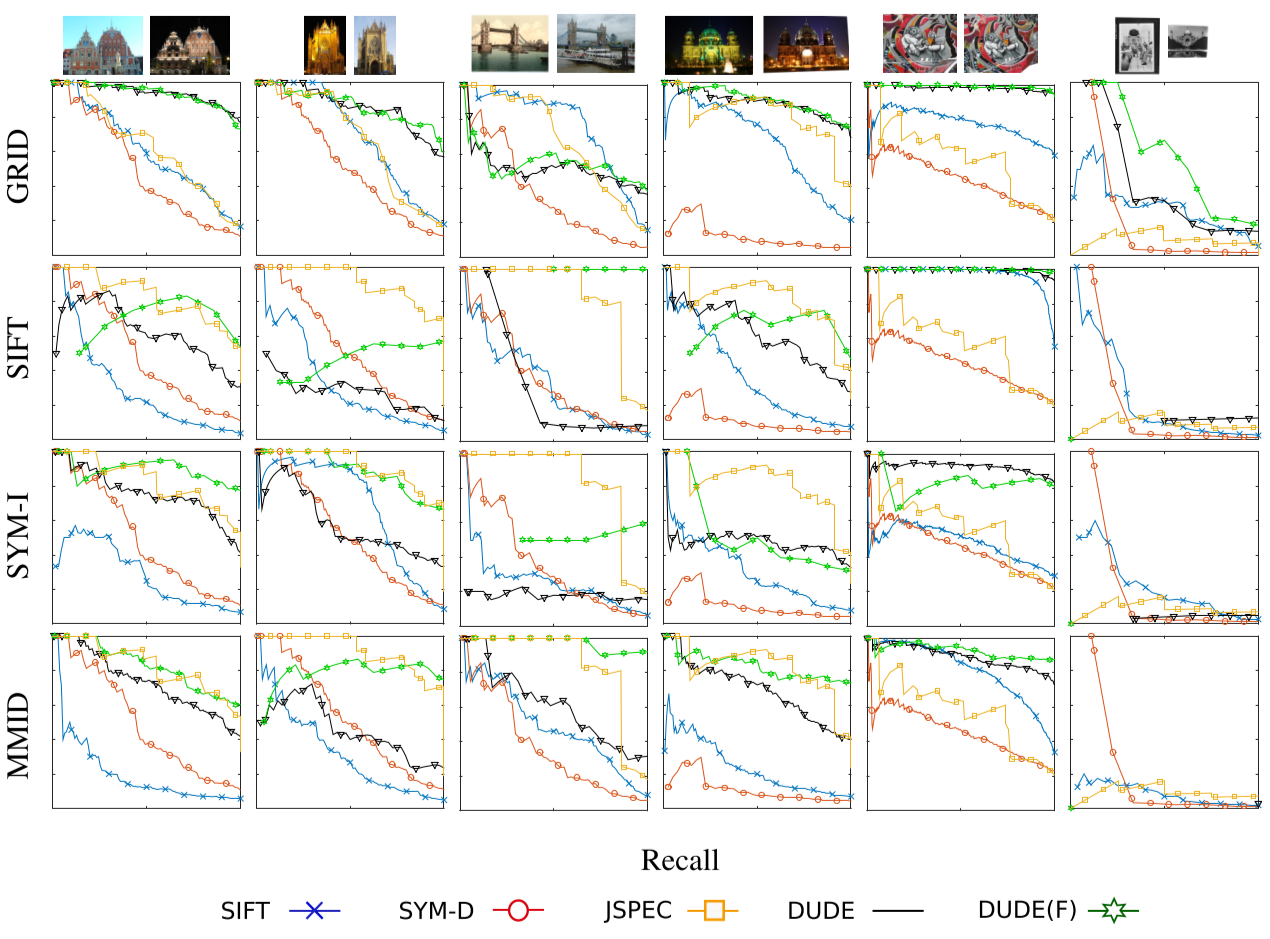
- Precision-recall curves for descriptor performance In the figure below, we illustrate precision-recall curves for a few image pairs. The choice example image pairs are the same as in [3]. Each row represents a feature detection type. DUDE (black) and DUDE-F (green) show overall good performance except for the last image pair, where most of algorithms do not work well. However, when detection is perfect (GRID), DUDE and DUDE-F outperform their competitors. Because DUDE-F has one more step than DUDE, it is natural for DUDE-F to be better than DUDE.
reference
Youngwook Paul Kwon, Hyojin Kim, Goran Konjevod, and Sara McMains, "DUDE (DUality DEscriptor): A Robust Descriptor for Disparate Images Using Line Segment Duality", IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2016. Bibtex
updated on May 9, 2016